This article aims to provide a concise and comprehensive overview of the carbon market tailored for business leaders, enabling them to seize opportunities and formulate the right strategies for their organizations.
climate change
Climate change refers to the negative shifts in global weather patterns caused by the Earth’s warming due to the greenhouse effect. This occurs when gases like CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O accumulate in the atmosphere. The primary driver of these changes is human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and agricultural practices.

carbon credit
A carbon credit is a certificate representing the reduction or removal of one ton of CO₂ from the atmosphere. These credits are generated through projects that absorb greenhouse gases, like reforestation, carbon capture and storage initiatives, or improvements in industrial processes to reduce emissions. Carbon credits can be traded as financial instruments, allowing companies or countries to offset their carbon footprint.
carbon pricing
Understanding carbon credit pricing involves viewing it as a commodity governed by production costs, quality, and supply-demand dynamics. Further analysis of these price components will be covered in a separate article.
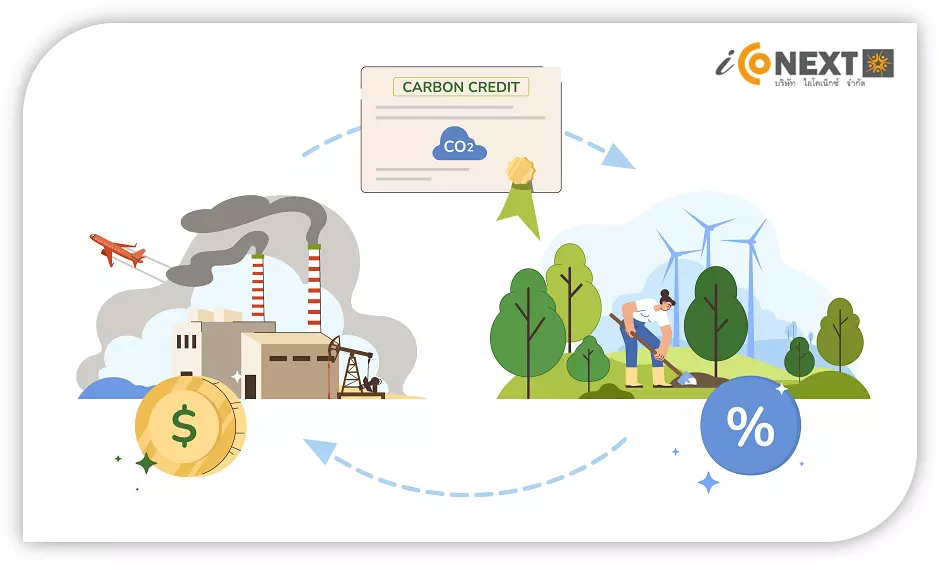
carbon market
The carbon market is where carbon credits are traded, allowing nations, companies, and organizations to buy and sell credits to achieve lower emissions targets. Entities that exceed their emission limits can purchase credits from projects that reduce emissions, thereby incentivizing global emission reductions.
The carbon market is divided into two main types:
- Compliance Markets: Operate in regions or countries with mandatory emission limits, like the European Union’s Emission Trading System (EU ETS). Here, governments impose caps, and companies must buy credits if they exceed these limits.
- Voluntary Markets: Allow companies to voluntarily purchase credits to offset emissions, often for companies with strong ESG strategies aiming to enhance sustainable branding.
carbon credit farming
To generate carbon credits, projects must adhere to specific standards. In Vietnam, potential projects include reforestation, renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, or waste treatment technologies. Projects must undergo a process of registration, monitoring, verification by third parties, and credit issuance, following standards like Gold Standard, Verra (VCS), or the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM).
Not all emission reductions qualify for carbon credits; only those meeting stringent standards and transparent reporting requirements are certified, ensuring credibility in trading.







